Create a GitHub Repository
Last updated on 2025-06-12 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I create a new repository on GitHub?
- How do I clone the repository to my local computer?
Objectives
- Create
multiverserepository on GitHub - Clone the
multiverserepository using VS Code
When the workshop begins, you should be sharing your screen, and instruct the learners to make sure their setup looks like yours:
- A new VS Code window is open (taking up the left 75% of the screen)
- A browser window with GitHub is open (taking up the right 75% of the screen)
In your browser window, you can have a second tab open with all images for this workshop, available at this URL
Create a new repo on GitHub
The first thing we need to do is create a new repository. While you can create repositories locally, and never even connect the local repo to a remote repo (hosted on a site like GitHub), the simplist and most common pattern to first create a new repo on GitHub, and then clone that repo to your local computer.
You should already be signed in to GitHub. You can create a new repo from anywhere on the site by clicking on the “+” icon in the upper right, and then clicking “New Repository”:
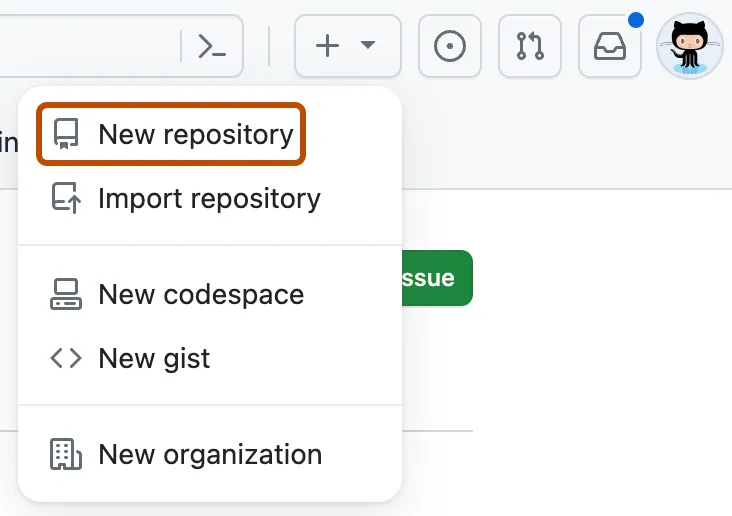
Select your Github username as the “owner”.
Type multiverse for the repository name.
Check the box next to “Add a README file”.
Leave all other options as the default - your repo should be public, no gitignore selected, no license selected, and no template selected.
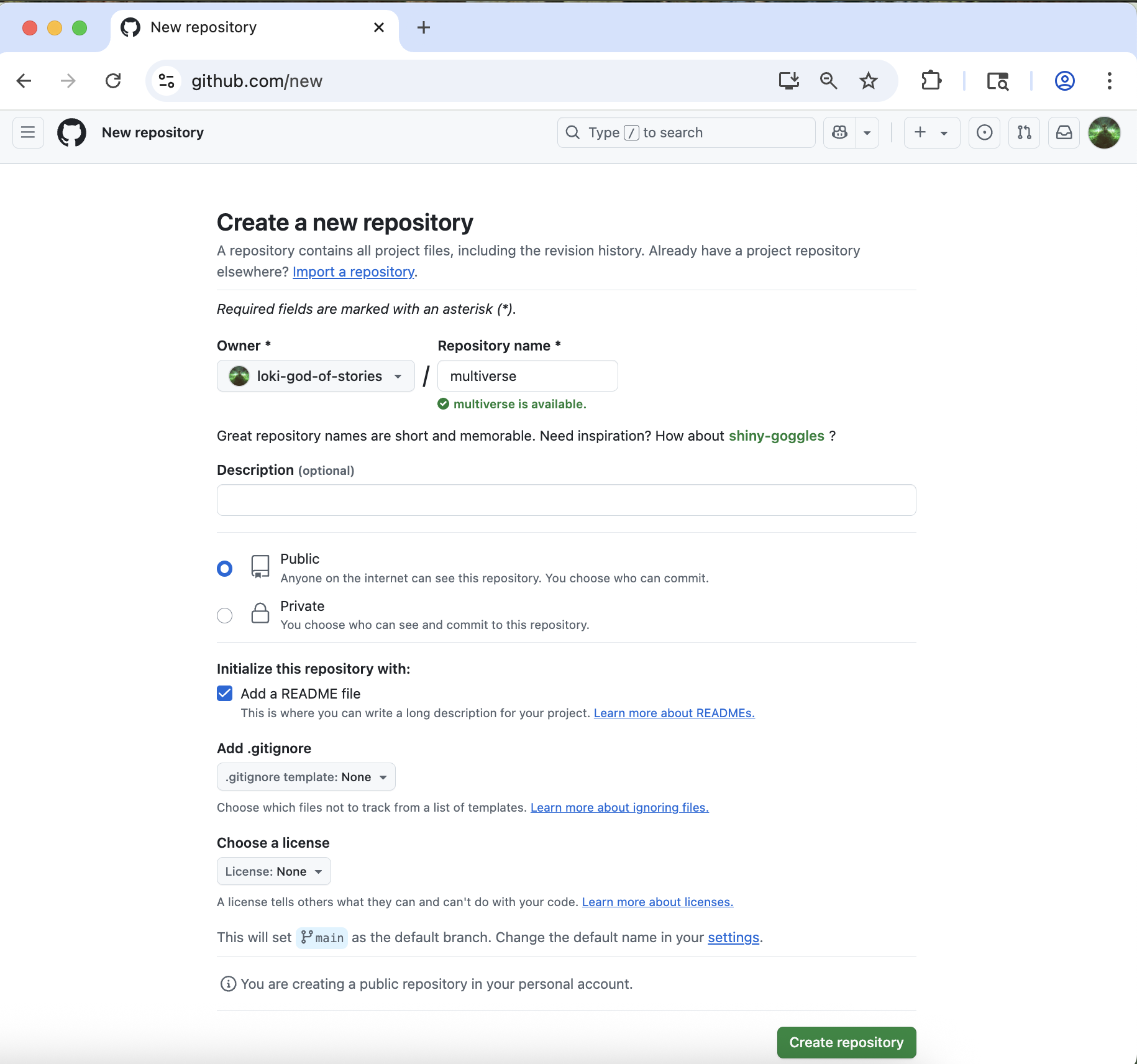
Finally, click the green “Create Repository” button at the bottom right.
You will be redirected to your newly created and empty
multiverse repo.
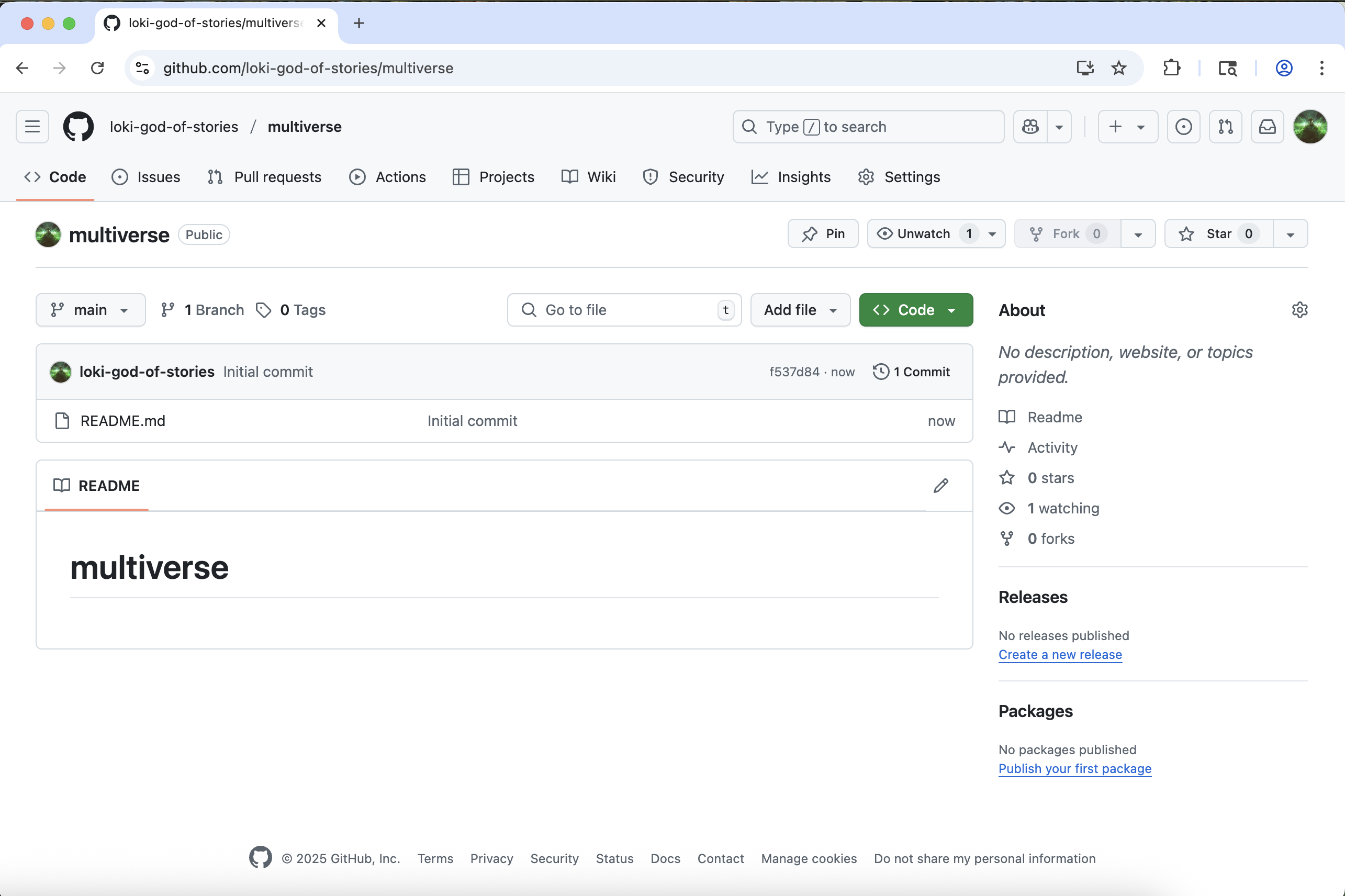
Clone your multiverse repo to your local computer
Now that the multiverse repo has been created, we can
“clone” it (get a local copy of the repo) through the command line (or
bash terminal).
Linux and Mac computers have “Terminal” applications. Windows computers need “Git Bash” installed. People refer to the terminal in various ways but they are all synonamous. All these terms refer to the same thing: terminal, bash, bash shell, bash terminal, console, the shell.
Open a Bash Terminal
If you can’t see the an icon for the terminal at the bottom of your screen you should be able to find it from the Menu button (on Linux), Start button (on Windows) or Apps button (on Mac).
The terminal usually opens up in your “home directory” or “home
folder”, indicated by a prompt which will be something along the lines
of /home/yourname$, /user/yourname$ or
~$. These prompts are very configurable and might look
different on different computers. The $ is usually
associated with the “Bash Shell” (there are many other shells) and the
~ is a shortcut for your home directory. You can always
determine which directory you are in by typing pwd after
the prompt and then pressing enter.
We want to clone the multiverse repo into our home
directory. When cloning, a new directory will be created, usually with
the same name as the repository.
Navigate to the terminal that you opened and type at the prompt
(replacing
Press enter to execute the command you just type. The following two line should be the resultant output.
Cloning into 'multiverse'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.You should now have your empty multiverse repo open,
with a Bash terminal open, and you are ready to start typing your first
git commands!
- Create a new repository on GitHub
- Clone the repository to your local computer
- Opening a bash terminal
